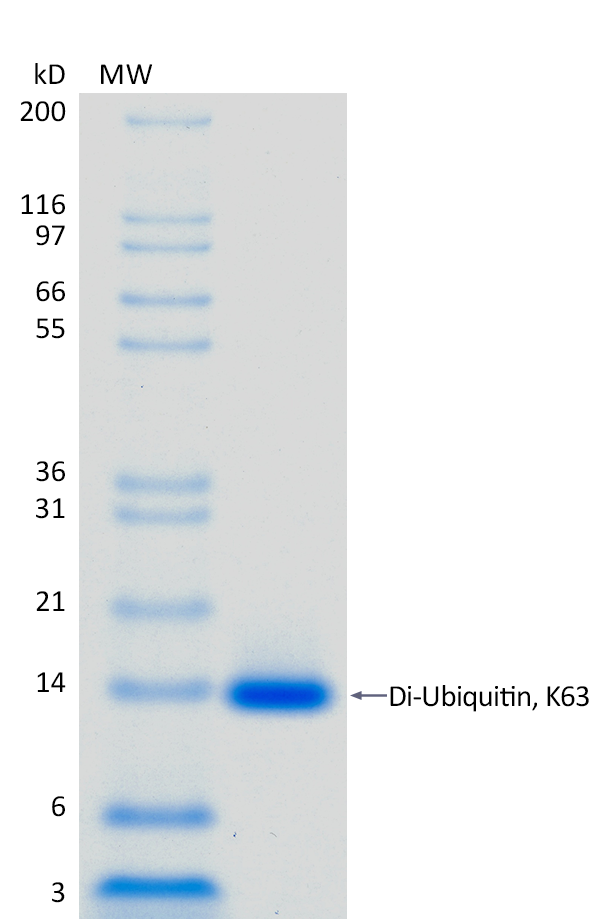
 2 μg K63-linked Di-Ubiquitin run on 4-12% SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions, then visualized with Colloidal Coomassie Blue Stain.
2 μg K63-linked Di-Ubiquitin run on 4-12% SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions, then visualized with Colloidal Coomassie Blue Stain.For Research Use Only (RUO)
Yoshikawa, A., et al., (2009) FEBS Lett 583:3317-22. PMID 19766637
Liu, Z., et al., (2015) eLife 4:e05767. PMID 26090905
Cao, L., et al., (2022) Cell Death Discov 8:410. PMID 36202787