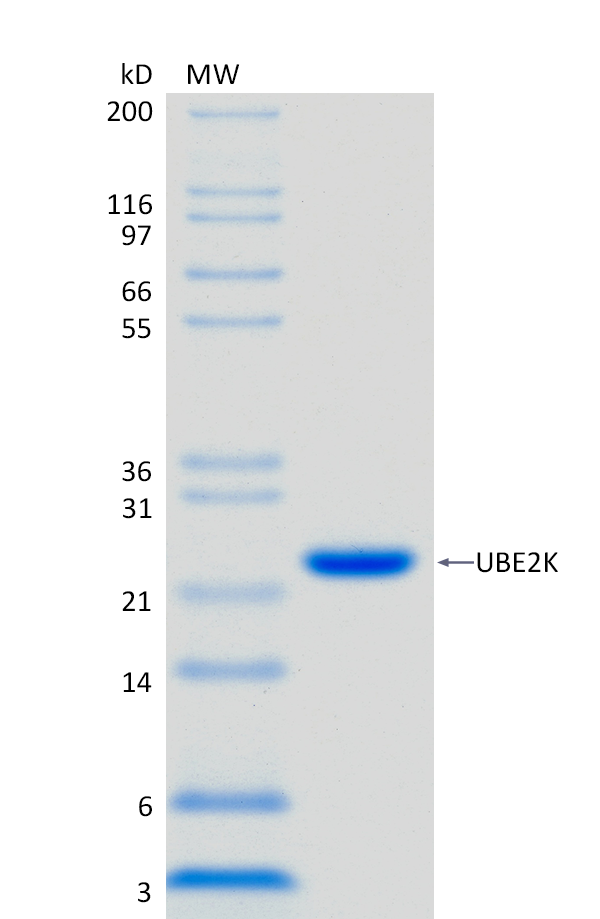
 2 μg UBE2K run on 4-12% SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions, then visualized with Colloidal Coomassie Blue Stain.
2 μg UBE2K run on 4-12% SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions, then visualized with Colloidal Coomassie Blue Stain.For Research Use Only (RUO)
Pluska, L., et al., (2021) EMBO J 40:e106094. PMID 33576509
Nakasone, M. A., et al., (2022) Nat Chem Biol 18:422-431. PMID 35027744